
Shutterstock
Kayleen Manwaring, UNSW and Peter Leonard, UNSW
The Internet of Things (IoT) is already all around us. Online devices have become essential in industries from manufacturing and healthcare to agriculture and environmental management, not to mention our own homes. Digital consulting firm Ovum estimates that by 2022 Australian homes will host more than 47 million IoT devices, and the value of the global market will exceed US$1 trillion.
The IoT presents great opportunities, but it brings many risks too. Problems include excessive surveillance, loss of privacy, transparency and control, and reliance on unsafe or unsuitable services or devices.
Read more:
Explainer: the Internet of Things
In some places, such as the European Union, Germany, South Korea and the United Kingdom, governments have been quick to develop policies and some limited regulation to take advantage of the technology and mitigate its harmful impacts.
Australia has been late to react. Even recent moves by the federal government to make IoT devices more secure have been far behind international developments.
A report launched today by the Australian Council of Learned Academies (ACOLA) may help get Australia up to speed. It supplies a wide-ranging, peer-reviewed base of evidence about opportunities, benefits and challenges the IoT presents Australia over the next decade.
Benefits of the Internet of Things
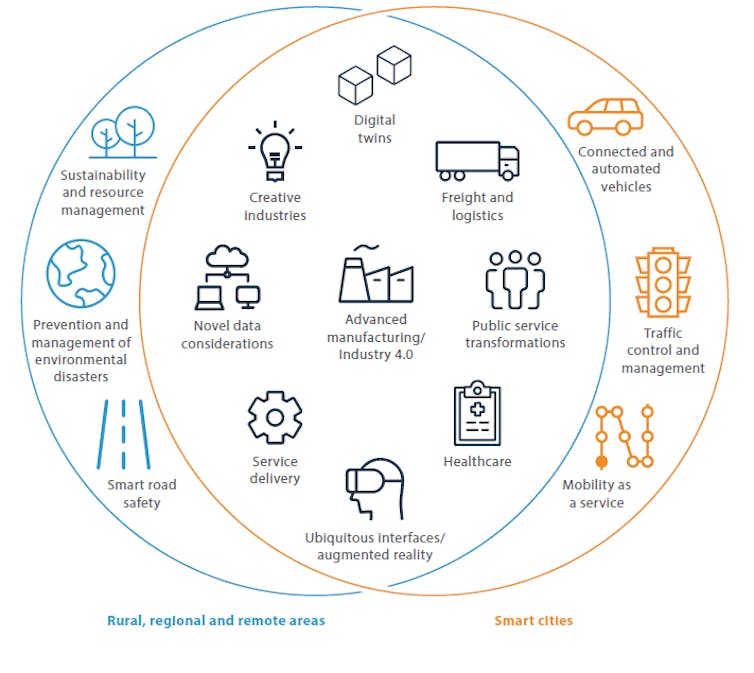
The report examines how we can improve our lives with IoT-related technologies. It explores a range of applications across Australian cities and rural, regional and remote areas.
Some IoT services are already available, such as the Smart Cities and Suburbs program run by local and federal governments. This program funds projects in areas such as traffic congestion, waste management and urban safety.
Health applications are also on the rise. The University of New England has piloted the remote monitoring of COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms using IoT-enabled pulse oximeters.
Augmented and virtual reality applications too are becoming more common. IoT devices can track carbon emissions in supply chains and energy use in homes. IoT services can also help governments make public transport infrastructure more efficient.
The benefits of the IoT won’t only be felt in cities. There may be even more to be gained in rural, regional and remote areas. IoT can aid agriculture in many ways, as well as working to prevent and manage bushfires and other environmental disasters. Sophisticated remote learning and health care will also benefit people outside urban areas.
ACOLA, CC BY-NC
Opportunities for the Australian economy
The IoT presents critical opportunities for economic growth. In 2016-17, IoT activity was already worth A$74.3 billion to the Australian economy.
The IoT can facilitate more data-informed processes and automation (also known as Industry 4.0). This has immediate potential for substantial benefits.
One opportunity for Australia is niche manufacturing. Making bespoke products would be more efficient with IoT capability, which would let Australian businesses reach a consumer market with wide product ranges but low domestic volumes due to our small population.
Agricultural innovation enabled by the IoT, using Australia’s existing capabilities and expertise, is another promising area for investment.
Read more:
Six things every consumer should know about the ‘Internet of Things’
Risks of the Internet of Things
IoT devices can collect huge amounts of sensitive data, and controlling that data and keeping it secure presents significant risks. However, the Australian community is not well informed about these issues and some IoT providers are slow to explain appropriate and safe use of IoT devices and services.
These issues make it difficult for consumers to tell good practice from bad, and do not inspire trust in IoT. Lack of consistent international IoT standards can also make it difficult for different devices to work together, and creates a risk that users will be “locked in” to products from a single supplier.
In IoT systems it can also be very complex to determine who is responsible for any particular fault or issue, because of the many possible combinations of product, hardware, software and services. There will also be many contracts and user agreements, creating contractual complexity that adds to already difficult legal questions.
Read more:
Are your devices spying on you? Australia’s very small step to make the Internet of Things safer
The increased surveillance made possible by the IoT can lead to breaches of human rights. Partially or fully automated decision-making can also to discrimination and other socially unacceptable outcomes.
And while the IoT can assist environmental sustainability, it can also increase environmental costs and impacts. The ACOLA report estimates that by 2050 the IoT could consume between 1 and 5% of the world’s electricity.
Other risks of harmful social consequences include an increased potential for domestic violence, the targeting of children by malicious actors and corporate interests, increased social withdrawal and the exacerbation of existing inequalities for vulnerable populations. The recent death of a woman in rural New South Wales being treated via telehealth provides just one example of these risks.
Maximising the benefits of the IoT
The ACOLA report makes several recommendations for Australia to take advantage of the IoT while minimising its downsides.
ACOLA advocates a national approach, focusing on areas of strength. It recommends continuing investment in smart cities and regions, and more collaboration between industry, government and education.
ACOLA also recommends increased community engagement, better ethical and regulatory frameworks for data and baseline security standards.
The ACOLA report is only a beginning. More specific work needs to be done to make the IoT work for Australia and its citizens.
The report does outline key areas for future research. These include the actual experiences of people in smart cities and homes, the value of data, environmental impacts and the use of connected and autonomous vehicles.![]()
Kayleen Manwaring, Senior Lecturer, School of Taxation & Business Law, UNSW and Peter Leonard, Professor of Practice (IT Systems and Management and Business and Taxation Law), UNSW Business School, Sydney, UNSW
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.


You must be logged in to post a comment.