Christiaan De Beukelaer, University of Melbourne
It has been rightly described as a humanitarian crisis and a modern form of forced labour.
In the early months of 2020, stranded cruise ships became a stark symbol of the COVID-19 global pandemic. Now it is seafarers stranded on cargo ships.
There are more than 50,000 such vessels, with about 1.6 million crew.
Before the coronavirus crisis, about 100,000 of these crew changed over each month, typically after serving contracts capped at 11 months under the United Nations Maritime Labour Convention. But since March, border closures and other restrictions have prevented this for many seafarers, forcing them into indefinite service, unable to even take shore leave.
And their work has never been more important to the rest of us. Before the pandemic cargo ships carried about 80% of all global trade. With the curtailment of international air travel reducing air cargo capacity by about 20%, shipping has become even more crucial to the global economy.
But the personal costs are enormous. Working on a cargo ship is taxing as the best of times. Now the work is even harder, with no respite.
Read more:
The reality of life for seafarers like those crewing the ‘hijacked’ tanker Nave Andromeda
In June the number of stranded seafarers was estimated to be 150,000. By September it was 400,000 (there are no more recent estimates). Some crew have now been at sea for 18 months.
The damage to mental health is great, increasing the risk of occupational accidents and environmental disasters.
Stuck at sea
Their plight is one to which I can personally relate.
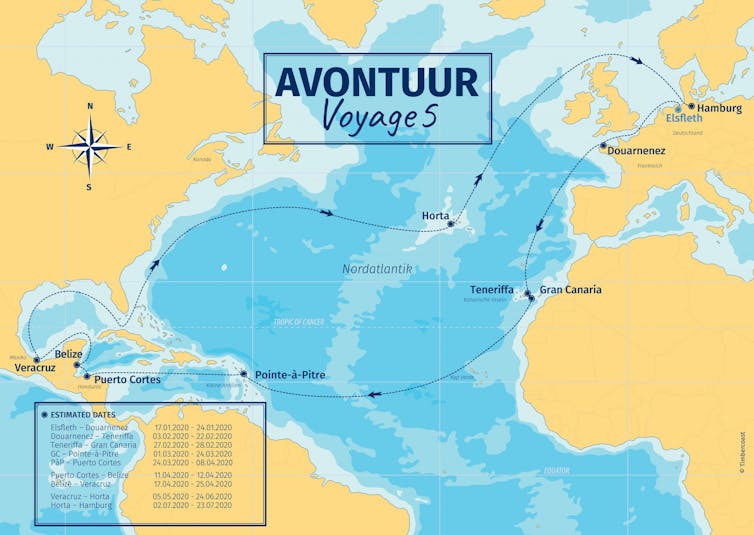
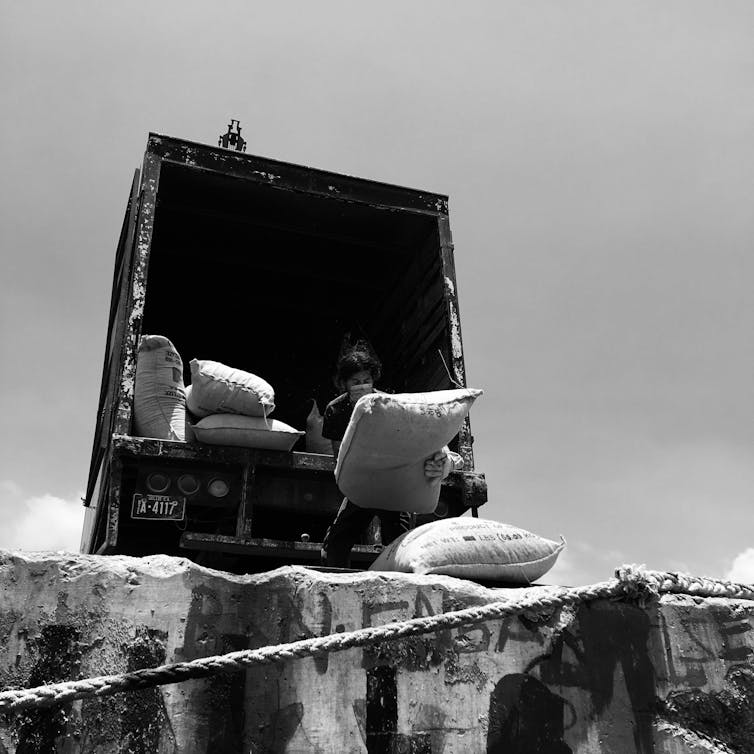
In early March I boarded a two-masted schooner, the Avontuur, one of the few cargo ships operating under sail, as part of my research into decarbonising the shipping industry. I planned to be on board for a three-week voyage from Tenerife in the Canary Islands to Guadeloupe in the Caribbean.
www.timbercoast.com
I ended up being on board for five months.
By the time we reached port at Point-à-Pitre in Guadeloupe, Caribbean nations were restricting air travel and closing borders due to COVID-19. On March 24, after extended negotiations, we were allowed to briefly dock to take provisions. But no one was allowed ashore.
On April 10, we reached Puerto Cortés in Honduras, to load a cargo of green coffee. Stevedores came aboard to load the bags, but we were prohibited from going ashore. A week later we loaded cacao in Belize City, but again were refused permission to step on land.

Christiaan De Beukelaer
So my trip extended port after port.
We spent ten days off the Mexican port of Veracruz, waiting for cargo, repairs and favourable winds. Again authorities did not allow us to step ashore. It wasn’t until late June, after more than 120 days on board, in Horta, that we were able to go ashore for a few days on the Azorean island of Faial. But given travel restrictions, we continued on for another three weeks to Hamburg.
The routine of work on a sailing ship occupied our time. Everyone worked eight hours a day in three different watches (four hours on, eight hours off).
But my ordeal was limited. I had confidence that in Hamburg I would be able to disembark and return to Australia. This is something many seafarers do not have. For many, there is still no light at the end of the tunnel.
Crew change possible, but difficult
Cargo ship crews need to keep watch and maintain the vessel at all times. They work 12 hours a day. Without weekends. Without seeing family or friends. Shore leave is increasingly rare, due to tight turnaround times in port, and often confined to docks.

Avigator Fortuner/Shutterstock
Labour unions and seafarers initially accepted crew change limitations due to COVID-19 border closures as “force majeure” – an issue beyond anyone’s control. As a result, flag states, unions, and port state authorities allowed ship owners to extend contracts beyond Maritime Labour Convention rules.
Since May, many organisations have been appealing to governments to recognise seafarers as “key workers” and permit them to cross borders. Ship owners have also been under fire for not doing enough.
Read more:
Thousands of seafarers are stranded aboard ships, with no end to their shift in sight
In early September the head of the International Maritime Organisation, Kitack Lim, said progress was being made by many countries in allowing for crew changes, but not at a rate to keep pace with the backlog.
Most nations now permit seafarers to cross borders, but the process is hampered by bureaucracy, screening and quarantine requirements, limited and hugely expensive air travel, and changing rules due to new waves of COVID-19. So while travelling home is technically possible, many seafarers remain stuck at sea.
The consequences, Kitack Lim warned, are dire:
Seafarers cannot remain at sea indefinitely. In addition to the humanitarian crisis that has been caused by keeping seafarers effectively trapped on their vessels, the safety issues that arise from requiring overly fatigued and mentally exhausted seafarers to continue operating vessels are a matter of great concern.
These concerns have been echoed by the Consumer Goods Forum, comprising the top executives of about 400 multinational retailers and manufacturers, which wrote to United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres calling for action to end a situation that had “inadvertently created a modern form of forced labor.”
The International Transport Workers’ Federation called the shipping industry “a ticking timebomb”, with its survey of seafarers showing 60% believed they or crew mates were more likely than not to be “involved in an accident that could harm human life, property or the marine environment due to tiredness or fatigue”.

Gwendoline Defente/AP
United Nations call for action
Where I live, the Australian Maritime Safety Authority announced last month it would end interim arrangements permitting seafarers to serve longer than 11 months on ships from 28 February 2021.
But as the International Transport Workers’ Federation noted – welcoming the decision while also expressing disappointment at the unnecessary delay – this is only the start of action needed from port states to help resolve the crew change crisis.
On December 1, the United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution calling on all governments to promptly take steps to facilitate crew changes, including by expediting travel and repatriation efforts and ensuring access to medical care.
A key step is designating seafarers as essential workers, with permission to cross borders, priority access to international flights, and to vaccinations when they become available.
The urgency is clear: the global economy depends on the work of seafarers.
When we celebrate Christmas with family and friends, feasting on imported delicacies and exchanging gifts shipped in from overseas, let’s not forget the ordeal of the hundreds of thousands stranded far from home who made that possible.![]()
Christiaan De Beukelaer, Senior Lecturer, University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.


You must be logged in to post a comment.