
Shutterstock
Laurie Berg, University of Technology Sydney and Bassina Farbenblum, UNSW
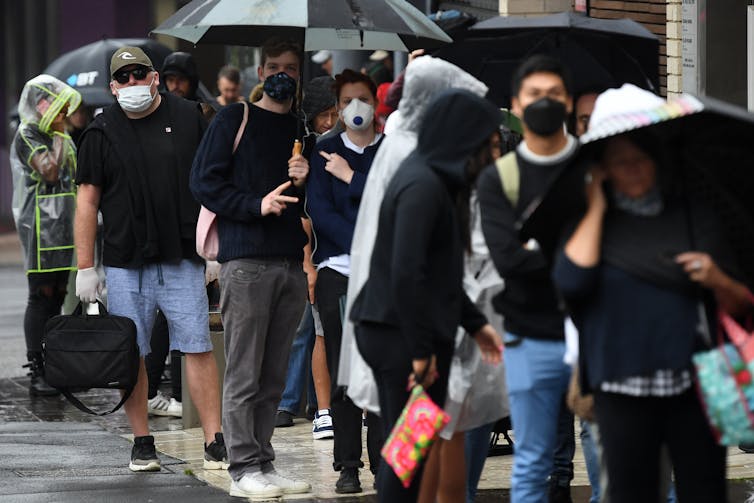
In the early days of the COVID-19 lockdown in March, many temporary visa holders working in heavily casualised industries, such as hospitality and retail, lost their jobs and struggled to meet basic living expenses.
These included international students, backpackers, graduates, sponsored workers and refugees, among others.
Despite the devastating financial impact on these temporary migrants, the government excluded them from JobKeeper and JobSeeker. Instead, Prime Minister Scott Morrison said if they could not support themselves, it was time to go home.
Today, UnionsNSW is releasing the findings of a large-scale survey showing just how badly temporary migrants have suffered due to the lockdown and lack of financial support from the government. The survey of over 5,000 visa holders, conducted in late March and early April, paints a devastating picture:
-
65% of participants lost their job
-
39% did not have enough money to cover basic living expenses
-
43% were skipping meals on a regular basis
-
34% were already homeless, or anticipated imminent eviction because they could not pay rent.
For many, a worsening financial situation
Data from a separate new survey we are conducting confirms that the financial hardship of temporary migrants is likely to worsen in the coming months.
Through the UTS and UNSW-led Migrant Worker Justice Initiative, we conducted an online survey of over 6,000 temporary migrants in July. Preliminary analysis indicates that over half of the participants (57%) anticipated their financial situation would be somewhat or much worse within six months.
This does not take into account the impact of the stage 4 lockdown in Victoria, which came into effect in August after our survey.
Read more:
Why temporary migrants need JobKeeper
Many respondents also said they could not “make their way home” when restrictions were being put in place to contain the virus — as Morrison had recommended — because flights were unavailable (20%) or unaffordable (27%). Others could not return because their country’s borders were closed (20%).
But for the majority, leaving Australia was not an option because of the great investment they said they had made in their studies (57%), their work and their futures in Australia (31%).
Half of our respondents also chose not to leave because they might not be able to return to Australia soon, or at all, and this was a risk they could not take.
The government’s treatment of temporary visa holders during the crisis also soured many on their experience here. According to our survey, 59% of international students and backpackers were now somewhat or far less likely to recommend Australia as a place for study or a working holiday.
One international student described his experience as
hopeless, lonely, wronged and without any support after five years paying my taxes and being part of the community.
And according to a backpacker,
the Australian government treated people on working holiday visas as consumable. If I go back to my country, I will never come to Australia again.
Calls for government support have been ignored
In early April, 43 leading academic experts across Australia warned of the severe humanitarian impact the lack of government support would have on visa holders who stayed in Australia.
As the level of destitution among temporary migrants became clear, charities tried to provide emergency food relief, and states introduced limited support schemes for international students, refugees and other groups of visa holders. Many universities, themselves facing significant financial challenges, also provided modest payments to international students.
Read more:
Open letter to the prime minister: extend coronavirus support to temporary workers
Despite these interventions, hundreds of organisations — including unions, refugee service providers and migrant communities — raised the alarm in May, and again in July, about the worsening humanitarian crisis.
Still, the federal government continues to refuse support for temporary migrants, except for a small, one-off emergency payment provided to the Red Cross for a limited number of visa holders.
The government’s only other concession was to permit temporary visa holders to access their superannuation (which most did not have because they worked for noncompliant employers who underpaid them in cash). Even this small support mechanism was recently ended for temporary residents without warning.

JOEL CARRETT/AAP
Why Australia must support temporary migrants
Australia is a global outlier in its callous treatment of temporary migrants during the pandemic. Other countries, such as the United Kingdom, New Zealand, Canada and Ireland, have all extended wage subsidies to temporary visa holders.
Australia has obligations under international human rights law to ensure every person within its borders has a safe and secure place to live, adequate food and basic health care.
Advising temporary visa holders to go home does not diminish these obligations. Nor does it absolve Australia of its moral obligations to these people it encouraged to greatly invest in studying and working here.
It is unreasonable to expect international students to simply abandon their studies, or to expect other migrants to leave Australia when it has become their home. They have paid tax, contributed to our community and built long-term relationships.
Many of Australia’s low-wage industries are also reliant on migrant workers. In fact, during the lockdown, the government even changed the rules of student visas to permit them to work more hours in dangerous jobs in aged care, supermarkets, disability support and health care.
The government should also be concerned about the reputational damage to our international education market, and to the working holiday maker market, which provides a critical labour force for the horticulture industry.
Over the coming months, without ongoing government support, the living situations for hundreds of thousands of temporary visa holders in Australia will continue to deteriorate.
It is well past time the federal government acknowledge this crisis and focus its attention on meeting temporary migrants’ acute humanitarian needs.
Read more:
The coronavirus risk Australia is not talking about: testing our unlawful migrant workers
![]()
Laurie Berg, Associate Professor, University of Technology Sydney and Bassina Farbenblum, Associate professor, UNSW
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.



You must be logged in to post a comment.