
Archa Fox, The University of Western Australia; Jen Martin, The University of Melbourne, and Traude Beilharz, Monash UniversityThe Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are set to become the mainstay of Australia’s COVID-19 vaccine rollout as the year progresses, according to the latest government projections released this week.
From September, up to an average 1.3m doses of the Pfizer vaccine plus another 125,000 doses of the yet-to-be approved Moderna vaccine are expected to be available per week. These figures are set to rise from October, as use of the AstraZeneca vaccine drops.
Both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are mRNA vaccines, which contain tiny fragments of the genetic material known as “messenger ribonucleic acid”. And if social media is anything to go by, some people are concerned these vaccines can affect their genetic code.
Here’s why the chances of that happening are next to zero and some pointers to how the myth came about.
Remind me, how do mRNA vaccines work?
The technology used in the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines is a way of giving your cells temporary instructions to make the coronavirus spike protein. This protein is found on the surface of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The vaccines teach your immune system to protect you if you ever encounter the virus.
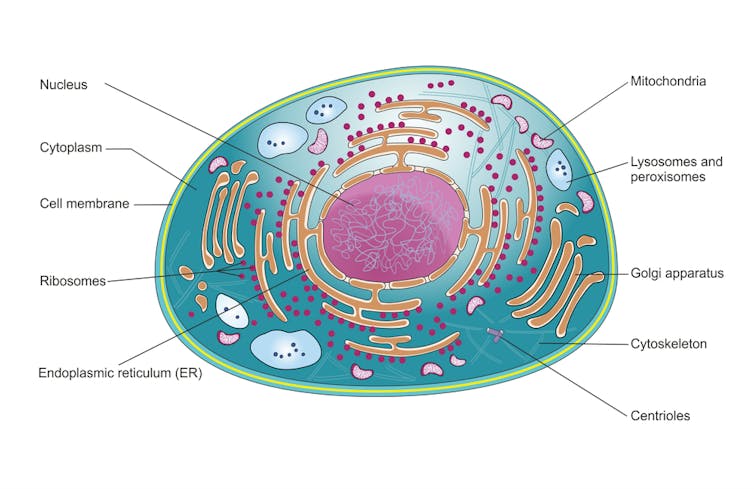
The mRNA in the vaccine is taken up by the cells in your body, ending up in the liquid inside each cell known as the cytoplasm. Our cells naturally make thousands of our own mRNAs all the time (to code for a range of other proteins). So the vaccine mRNA is just another one. Once the vaccine mRNA is in the cytoplasm it’s used to make the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
The vaccine mRNA is short-lived and is rapidly broken down after it’s done its job, as happens with all your other mRNA.
www.shutterstock.com
Here’s why the mRNA can’t insert into your genetic code
Your genetic code is made up of a different, but related, molecule to the vaccine mRNA, known as DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid. And mRNA can’t insert itself into your DNA for two reasons.
One, both molecules have a different chemistry. If mRNAs could routinely insert themselves into your DNA at random, this would play havoc with how you produce proteins. It would also scramble your genome, which is passed on to future cells and generations. Life forms that do this would not survive. That’s why life has evolved for this not to happen.
The second reason is vaccine mRNA and DNA are in two different parts of the cell. Our DNA stays in the nucleus. But vaccine mRNA goes straight to the cytoplasm, never entering the nucleus. There are no transporter molecules we know of that carry mRNA into the nucleus.
But aren’t there some exceptions?
There are some extremely rare exceptions. One is where genetic elements, known as retro-transposons, hijack cellular mRNA, convert it into DNA and insert that DNA back into your genetic material.
This has occurred sporadically throughout evolution, producing some ancient copies of mRNAs scattered throughout our genome, to form so-called pseudogenes.
Some retroviruses, such as HIV, also insert their RNA into our DNA, using similar methods to retro-transposons.
However, there is a vanishingly small chance of a naturally occurring retro-transposon becoming active in a cell that has just received a mRNA vaccine. There’s also a vanishingly small chance of being infected with HIV at precisely the same time as receiving the mRNA vaccine.

from www.shutterstock.com
Even if a retro-transposon were to become active or a virus such as HIV were present, the chances of it finding the COVID vaccine mRNA, among the tens of thousands of natural mRNAs, is extremely unlikely. That’s because vaccine mRNA is degraded within several hours of entering the body.
Even if vaccine mRNA did become a pseudogene, it would not produce the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but just one of the viral products, the harmless spike protein.
Read more:
4 things about mRNA COVID vaccines researchers still want to find out
How do we actually know this?
We know of no studies looking for vaccine mRNA in the DNA of people who have been vaccinated. There is no scientific basis on which to suspect this insertion has happened.
However, if these studies were to be carried out, they should be relatively straightforward. That’s because we can now sequence DNA in single cells.
But in reality, it will be very hard to ever satisfy a naysayer who is convinced this genome insertion happens; they can always argue scientists need to look deeper, harder, in different people and in different cells. At some point this argument will need to be laid to rest.
So how did this myth come about?
One study reported evidence for coronavirus RNA integrating into the human genome in cells grown in the lab that had been infected with SARS-CoV-2.
However, that paper did not look at the mRNA vaccine, lacked critical controls and has since been discredited.
These types of studies also need to be seen in context of the public’s wariness of genetic technology more broadly. This includes the public’s concerns about genetically modified organisms (GMOs), for instance, over the past 20 years or so.
But GMOs are different to the mRNA technology used to make COVID vaccines.
Unlike GMOs, which are produced by inserting DNA into the genome, vaccine mRNA will not be in our genes or passed to the next generation. It’s broken down very quickly.
In reality, mRNA technology has all sorts of applications, beyond vaccines, including biosecurity and sustainable agriculture. So it would be a pity for these efforts to be held back by misinformation.
Archa Fox, Associate Professor and ARC Future Fellow, The University of Western Australia; Jen Martin, Leader, Science Communication Teaching Program, The University of Melbourne, and Traude Beilharz, Assoc Professor ARC Future Fellow, Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.







You must be logged in to post a comment.